파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰_배열
«파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰 서적 내용을 정리»
문제01 두 수의 합
https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum/
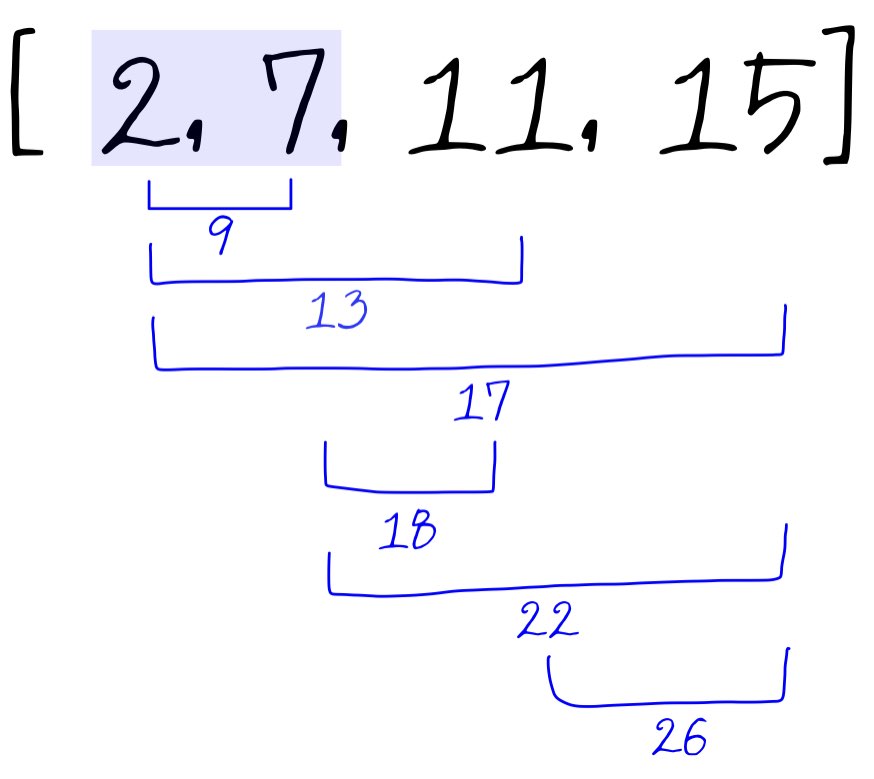
덧셈하여 타겟을 만들 수 있는 배열의 두 숫자 인덱스를 리턴하라.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9 Output: [0,1] Output: Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6 Output: [1,2]Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6 Output: [0,1]
- 풀이1_브루트 포스로 계산
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)):
if nums[i]+nums[j] == target:
return [i,j]
Result
Runtime : 40ms, Memory : 14.5MB
- 풀이2_in을 이용한 탐색
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
for i, n in enumerate(nums):
complement = target - n
if complement in nums[i+1:]:
return [nums.index(n), nums[i+1 :].index(complement)+(i+1)]
Result
Runtime : 36ms, Memory : 14.3MB
- 풀이3_첫 번째 수를 뺀 결과 키 조회
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
nums_map = {}
# 키와 값을 바꿔서 딕셔너리로 저장
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
nums_map[num] = i
# 타겟에서 첫 번째 수를 뺀 결과를 키로 조회
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
# 뺀 값이 딕셔너리에 있고, 그 값의 value가 i랑 같지 않다
#(ex. idx가 0인 숫자 5는 타겟인 10에 뺐을때 5가 남음 -> 여기서 5는 idx가 0인 숫자 5가 아닌 다른 인덱스의 숫자 5여야 함)
if target - num in nums_map and i != nums_map[target-num]:
return [i, nums_map[target-num]]
Result
Runtime : 40ms, Memory : 14.4MB
- 풀이4_조회 구조 개선
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
nums_map = {}
# 하나의 for문으로 통합
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
if target - num in nums_map:
return [nums_map[target-num], i]
nums_map[num] = i
Result
Runtime : 40ms, Memory : 14.2MB
- 풀이5_투 포인터 이용
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
nums.sort()
left, right = 0, len(nums)-1
while not left == right:
# 합이 타겟보다 작으면 왼쪽 포인터를 오른쪽으로
if nums[left] + nums[right] < target:
left += 1
# 합이 타겟보다 크면 오른쪽 포인터를 왼쪽으로
elif nums[left] + nums[right] > target:
right -= 1
else:
return [left, right]
Result
Wrong Answer : 투 포인터를 이용하려면 nums가 정렬이 필요. But 이 문제는 인덱스를 찾아내야하기 때문에 정렬하면 인덱스가 엉키게 됨.
문제02 빗물 트래핑
https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water
높이를 입력받아 비 온 후 얼마나 많은 물이 쌓일 수 있는지 계산하라.
Example 1:
Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] Output: 6 Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.Example 2:
Input: height = [4,2,0,3,2,5] Output: 9
- 풀이1_투 포인터를 최대로 이동
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
if not height:
return 0
volume = 0
# 투 포인트 초기화
left, right = 0, len(height)-1
# left_max, right_max값 초기화
left_max, right_max = height[left], height[right]
while left < right:
# 현재 가리키는 값 : height[left]과 현재 가장 큰 값 : left_max을 비교해 큰 값을 left_max로 초기화
left_max, right_max = max(height[left], left_max), max(height[right], right_max)
# 더 높은 쪽으로 향해 투 포인터 이동
if left_max <= right_max:
volume += left_max - height[left]
left += 1
else:
volume += right_max - height[right]
right -= 1
return volume
Result
Runtime : 52ms, Memory : 15MB
- 풀이2_스택 쌓기
class Solution:
def trap(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
stack = []
volume = 0
for i in range(len(height)):
# 변곡점을 만나는 경우(현재 높이:height[i]가 이전 높이:height[stack[-1]]보다 높을 때)
while stack and height[i] > height[stack[-1]]:
# 스택에서 꺼낸다
top = stack.pop()
if not len(stack):
break
# 이전과의 차이만큼 물 높이 처리
distance = i - stack[-1] -1
waters = min(height[i], height[stack[-1]]) - height[top]
volume += distance * waters
stack.append(i)
return volume
Result
Runtime : 64ms, Memory : 14.8MB
문제03 세 수의 합
https://leetcode.com/problems/3sum
배열을 입력받아 합으로 0을 만들 수 있는 3개의 엘리먼트를 출력하라.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] Output: [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]Example 2:
Input: nums = [] Output: []Example 3:
Input: nums = [0] Output: []
- 풀이1_브루트 포스로 계산
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
results = []
nums.sort()
# 브루트 포스 n^3 반복
for i in range(len(nums)-2):
# 중복된 값 건너뛰기
# 위에서 정렬했기 때문에 nums[i] == nums[i-1] 비교 가능
if i>0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
for j in range(i+1, len(nums)-1):
if j>i+1 and nums[j]==nums[j-1]:
continue
for k in range(j+1, len(nums)):
if k>j+1 and nums[k] == nums[k-1]:
continue
if nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0:
results.append((nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]))
return results
Result
Time Limit Exceeded
시간복잡도 O(n^3)으로 시간 초과
- 풀이2_투 포인터로 합 계산
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
results = []
nums.sort()
for i in range(len(nums)-2):
# 중복된 값 건너뛰기
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
# 간격을 좁혀가며 합 sum 계산
left, right = i+1, len(nums)-1
while left < right:
sum = nums[i]+nums[left]+nums[right]
if sum < 0:
left += 1
elif sum > 0:
right -= 1
else:
# sum = 0인 경우이므로 정답 및 스킵 처리
results.append((nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]))
while left < right and nums[left] == nums[left + 1]:
left += 1
while left < right and nums[right] == nums[right -1]:
right -= 1
left += 1
right -= 1
return results
Result
Runtime : 872ms, Memory : 16.8MB
투 포인터란?
시작점과 끝점 또는 왼쪽 포인터와 오른쪽 포인터 두 지점을 기준으로 하는 문제 풀이 전략을 의미한다.
일반적으로 배열이 정렬되어 있는 경우에 유용하게 사용이 가능하다. 슬라이딩 윈도우와 비슷하지만 차이점이 존재한다.
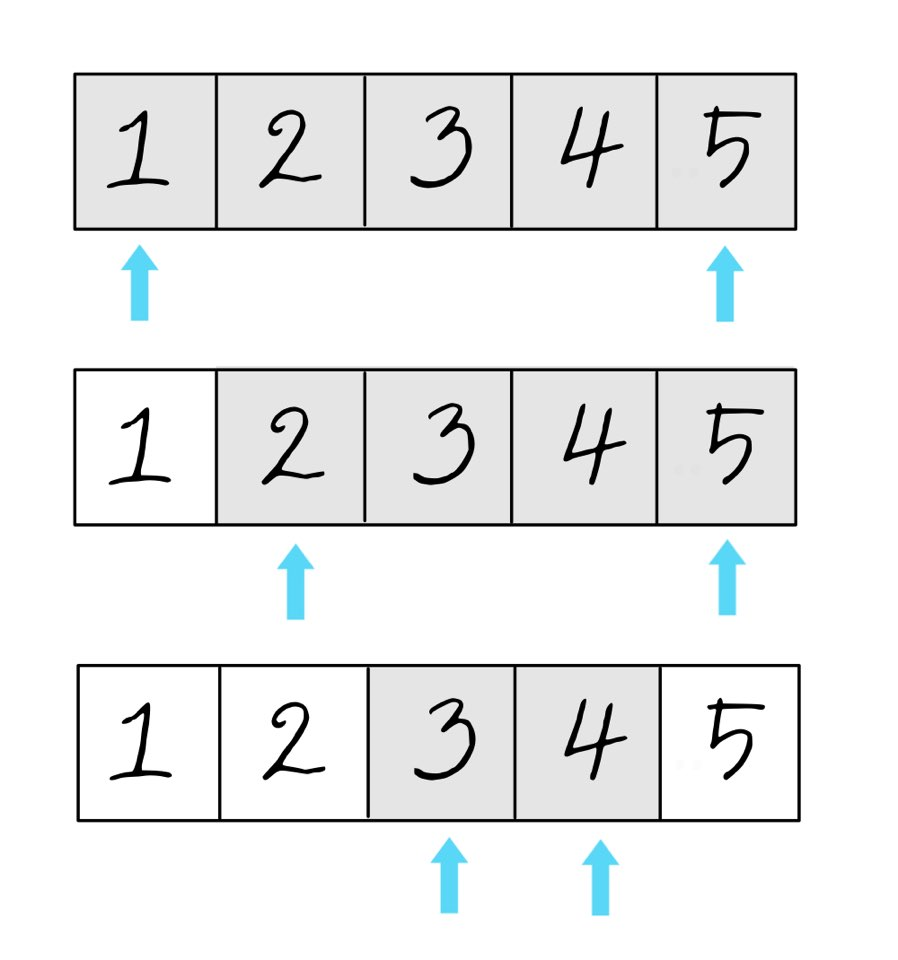
문제04 배열 파티션 I
https://leetcode.com/problems/array-partition-i
n개의 페어를 이용한 min(a, b)의 합으로 만들 수 있는 가장 큰 수를 출력하라.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,4,3,2] Output: 4 Explanation: All possible pairings (ignoring the ordering of elements) are: 1. (1, 4), (2, 3) -> min(1, 4) + min(2, 3) = 1 + 2 = 3 2. (1, 3), (2, 4) -> min(1, 3) + min(2, 4) = 1 + 2 = 3 3. (1, 2), (3, 4) -> min(1, 2) + min(3, 4) = 1 + 3 = 4 So the maximum possible sum is 4.Example 2:
Input: nums = [6,2,6,5,1,2] Output: 9 Explanation: The optimal pairing is (2, 1), (2, 5), (6, 6). min(2, 1) + min(2, 5) + min(6, 6) = 1 + 2 + 6 = 9.
- 내 풀이
class Solution:
def arrayPairSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
n = len(nums) // 2
nums.sort(reverse=True)
cnt, i, result = 0, 0, 0
while cnt < n:
result += min(nums[i:i+2])
i+=2
cnt+=1
return result
Result
Runtime : 288ms, Memory : 16.9MB
- 풀이1_오름차순 풀이
class Solution:
def arrayPairSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
sum = 0
pair = []
nums.sort()
for n in nums:
#앞에서부터 오름차순으로 페어를 만들어서 합 계산
pair.append(n)
if len(pair) == 2:
sum += min(pair)
pair = []
return sum
Result
Runtime : 320ms, Memory : 16.7MB
- 풀이2_짝수번째 값 계산
class Solution:
def arrayPairSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
sum = 0
nums.sort()
for i, n in enumerate(nums):
# 짝수 번째 값의 합 계산
if i%2 == 0:
sum += n
return sum
Result
Runtime : 264ms, Memory : 17MB
- 풀이3_파이썬 다운 방식
class Solution:
def arrayPairSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
return sum(sorted(nums)[::2])
Result
Runtime : 256ms, Memory : 16.9MB
문제05 자신을 제외한 배열의 곱
https://leetcode.com/problems/product-of-array-except-self
배열을 입력받아 output[i]가 자신을 제외한 나머지 모든 요소의 곱셈 결과가 되도록 출력하라.
주의) 나눗셈을 하지 않고 O(n)에 풀이하라.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,4] Output: [24,12,8,6]
- 풀이1_왼쪽 곱셈 결과에 오른쪽 값을 차례대로 곱셈
class Solution:
def productExceptSelf(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
out = []
p = 1
# 왼쪽 곱셈
for i in range(0, len(nums)):
out.append(p)
p = p * nums[i]
p = 1
# 왼쪽 곱셈 결과에 오른쪽 값을 차례대로 곱셈
for i in range(len(nums) -1, 0 - 1, -1):
out[i] = out[i] * p
p = p * nums[i]
return out
Result
Runtime : 220ms, Memory : 21.1MB
문제06 주식을 사고팔기 가장 좋은 시점
https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock
한 번의 거래로 낼 수 있는 최대 이익을 산출하라.
Example 1:
Input: prices = [7,1,5,3,6,4] Output: 5 Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5. Note that buying on day 2 and selling on day 1 is not allowed because you must buy before you sell.Example 2:
Input: prices = [7,6,4,3,1] Output: 0 Explanation: In this case, no transactions are done and the max profit = 0.
- 풀이1_브루트 포스로 계산
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
max_price = 0
for i, price in enumerate(prices):
for j in range(i, len(prices)):
max_price = max(prices[j] - price, max_price)
return max_price
Result
Time Limit Exceeded
시간복잡도 O(n^2)으로 시간 초과
- 풀이2_저점과 현재 값과의 차이 계산
class Solution:
def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int:
profit = 0
min_price = sys.maxsize
# 최솟값과 최댓값을 계속 갱신
for price in prices:
min_price = min(min_price, price)
profit = max(profit, price - min_price)
return profit
Result
Runtime : 1092ms, Memory : 25.2MB
파이썬에서 최댓값과 최솟값
# 최댓값과 최솟값 초깃값 설정
# 최댓값에는 가장 낮은 값을 초기값을 설정해야하고, 최솟값에는 가장 높은 값을 초깃값으로 설정해야 바로 값이 교체될 수 있다.
mx = -sys.maxsize
mn = sys.maxsize
