파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰_연결 리스트
«파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰 서적 내용을 정리»
- 문제01 팰린드롬 연결 리스트
- 문제02 두 정렬 리스트의 병합
- 문제03 역순 연결 리스트
- 문제04 두 수의 덧셈
- 문제05 페어의 노드 스왑
- 문제06 홀짝 연결 리스트
- 문제07 역순 연결 리스트 II
문제01 팰린드롬 연결 리스트
https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list
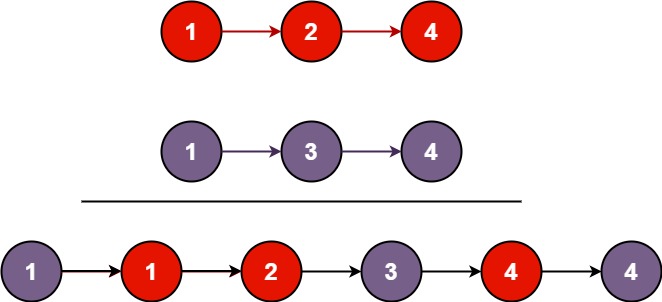
연결 리스트가 팰린드롬 구조인지 판별하라.
Example 1:
Input: 1->2 Output: falseExample 2:
Input: 1->2->2->1 Output: true
- 풀이1_리스트 변환
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
q: List = []
# linked list가 없는 경우
if not head:
return True
node = head
# 리스트 변환
while node is not None:
q.append(node.val)
node = node.next
# 팰린드롬 판별
while len(q) > 1:
if q.pop(0) != q.pop():
return False
return True
Result
Runtime : 168ms, Memory : 24.3MB
- 풀이2_데크를 이용한 최적화
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
# 데크 자료형 선언
q: Deque = collections.deque()
# linked list가 없는 경우
if not head:
return True
node = head
# 리스트 변환
while node is not None:
q.append(node.val)
node = node.next
# 팰린드롬 판별
while len(q) > 1:
if q.popleft() != q.pop():
return False
return True
Result
Runtime : 72ms, Memory : 24.3MB
풀이1의 문제점은 if q.pop(0) != q.pop():에서의 속도이다. 리스트는 동적 배열로 구성되어 맨 앞의 아이템을 가져오면 모든 값이 한 칸씩 시프팅이 이루어지면 시간복잡도는 O(n)이 발생한다. 이를 해결하기 위해 데크를 사용해 처리하면 빠르게 처리할 수 있다.

- 풀이3_런너를 이용한 우아한 풀이
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
rev = None
print(rev)
slow = fast = head
# 런너를 이용해 역순 연결 리스트 구성
while fast and fast.next:
print()
fast = fast.next.next
rev, rev.next, slow = slow, rev, slow.next
# 입력값이 홀수인 경우 slow런너를 한 칸 더 앞으로 이동하여 중앙값을 빗겨 나감(홀수의 경우 중앙값이 팰린드롬 체크에서 벗어나야함)
if fast:
slow = slow.next
# 팰린드롬 여부 확인
while rev and rev.val == slow.val:
slow, rev = slow.next, rev.next
return not rev
Result
Runtime : 68ms, Memory : 24.3MB
런너 기법
연결 리스트를 순회할 때 2개의 포이너를 동시에 사용하는 기법이다. 한 포인터가 다른 포인터보다 앞서게하여 병합 지점이나 중간 위치, 길이 등을 판별할 때 유용하게 사용함
빠른 런너(Fast Runner)는 주로 두 칸씩 건너뛰고 느린 런너(Slow Runner)는 주로 한 칸씩 이동하여 빠른 런너가 리스트 끝에 도달하면 느린 런너는 리스트의 중간 지점을 가리키게 되며 중간 위치를 찾아낸다.
문제02 두 정렬 리스트의 병합
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists
정렬되어 있는 두 연결 리스트를 합쳐라.
Example 1:
Input: l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]Example 2:
Input: l1 = [], l2 = [] Output: []Example 3:
Input: l1 = [], l2 = [0] Output: [0]
- 풀이1_재귀 구조로 연결
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if (not l1) or (l2 and l1.val > l2.val):
l1, l2 = l2, l1
if l1:
l1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2)
return l1
Result
Runtime : 36ms, Memory : 14.4MB
문제03 역순 연결 리스트
https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list
연결 리스트를 뒤집어라.
Example :
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL Output: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
- 내 코드
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
rev = None
slow = head
while slow:
rev, rev.next, slow = slow, rev, slow.next
return rev
Result
Runtime : 56ms, Memory : 15.5MB
문제1에서 런너 기법을 사용해 역순 연결리스트를 구성해 팰린드롬을 판별한 코드에서 느린 런너를 사용해 역순 연결 리스트를 구성해보았다.
- 풀이1_재귀 구조로 뒤집기
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
def reverse(node: ListNode, prev : ListNode = None):
if not node:
return prev
next, node.next = node.next, prev
return reverse(next, node)
return reverse(head)
Result
Runtime : 40ms, Memory : 20.2MB
- 풀이2_반복 구조로 뒤집기
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
node, prev = head, None
while node:
tmp, node.next = node.next, prev
prev, node = node, tmp
return prev
Result
Runtime : 40ms, Memory : 15.6MB
tmp : node의 다음 이동 지점 포인터
prev : 역순 연결 리스트 저장
node.next는 node가 연결될 node(prev)를 알려준는 역할
문제04 두 수의 덧셈
https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers
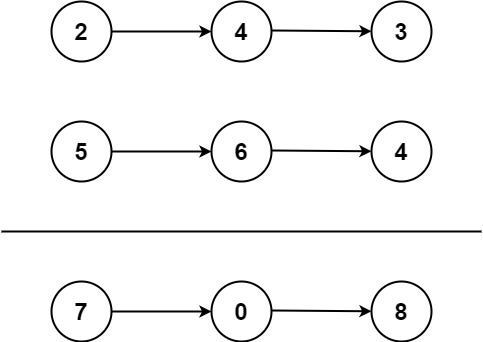
역순으로 저장된 연결 리스트의 숫자를 더하라.
Example 1:
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] Output: [7,0,8] Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0] Output: [0]Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
- 풀이1_자료형 변환
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
# 연결 리스트 뒤집기
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
node, prev = head, None
while node:
tmp, node.next = node.next, prev
prev, node = node, tmp
return prev
# 연결 리스트를 파이썬 리스트로 변환
def toList(self, node: ListNode) -> List:
list: List = []
while node:
list.append(node.val)
node = node.next
return list
# 파이썬 리스트를 연결 리스트로 변환
def toReverseLinkedList(self, result: str) -> ListNode:
prev : ListNode = None
for r in result:
node = ListNode(r)
node.next = prev
prev = node
return node
# 두 연결 리스트의 덧셈
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
a = self.toList(self.reverseList(l1))
b = self.toList(self.reverseList(l2))
resultStr = int(''.join(str(e) for e in a)) + int(''.join(str(e) for e in b))
# 최종 계산 결과 연결 리스트 변환
return self.toReverseLinkedList(str(resultStr))
Result
Runtime : 76ms, Memory : 14.4MB
- 풀이2_전가산기 구현
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
root = head = ListNode(0)
carry = 0
while l1 or l2 or carry:
sum = 0
# 두 입력값의 합 계산(자리수에 맞는 값 덧셈)
if l1:
sum += l1.val
l1 = l1.next
if l2:
sum += l2.val
l2 = l2.next
# 몫(자리올림수)과 나머지(값) 계산
carry, val = divmod(sum+carry, 10)
head.next = ListNode(val)
head = head.next
return root.next
Result
Runtime : 72ms, Memory : 14.2MB
숫자형 리스트를 단일 값으로 병합하기
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]처럼 숫자형으로 이루어진 리스트인 경우 하나로 합치는 효율적인 방법은?
① ‘‘.join(map(str, a))
map()을 이용해 숫자형을 문자열로 변환하여 출력한다.
하지만 애초에 숫자형으로 바로 변경하는 방법은?
② functools.reduce(lambda x, y : 10 * x + y, a, 0)
③ from operator import mul
functools.reduce(mul, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
문제05 페어의 노드 스왑
https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs
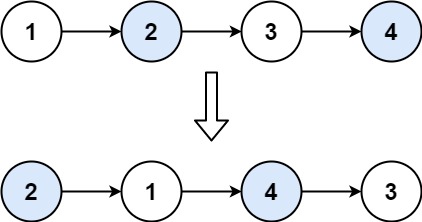
연결 리스트를 입력받아 페어 단위로 스왑하라.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4] Output: [2,1,4,3]Example 2:
Input: head = [] Output: []Example 3:
Input: head = [1] Output: [1]
- 풀이1_값만 교환
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur = head
while cur and cur.next:
# 값만 교환
cur.val, cur.next.val = cur.next.val, cur.val
cur = cur.next.next
return head
Result
Runtime : 32ms, Memory : 14.3MB
- 풀이2_반복 구조로 스왑
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
root = prev = ListNode(None)
prev.next = head
while head and head.next:
# b가 a(head)를 가리키도록 할당
b = head.next
head.next = b.next
b.next = head
# prev가 b를 가리키도록 할당
prev.next = b
# 다음번 비교를 위해 이동
head = head.next
prev = prev.next.next
return root.next
Result
Runtime : 28ms, Memory : 14.3MB
- 풀이3_재귀 구조로 스왑
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head and head.next:
p = head.next
# 스왑된 값 리턴 받음
head.next = self.swapPairs(p.next)
p.next = head
return p
return head
Result
Runtime : 28ms, Memory : 14.3MB
문제06 홀짝 연결 리스트
https://leetcode.com/problems/odd-even-linked-list
연결 리스트를 홀수 노드 다음에 짝수 노드가 오도록 재구성하라. (홀수 노드란 노드 값을 의미하는 것이 아닌 홀수 인덱스를 의미하는 것)
공간 복잡도 O(1), 시간 복잡도O(n)에 풀이하라.
Example 1:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL Output: 1->3->5->2->4->NULLExample 2:
Input: 2->1->3->5->6->4->7->NULL Output: 2->3->6->7->1->5->4->NULL
- 풀이1_반복 구조로 홀짝 노드 처리
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def oddEvenList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# 예외 처리
if head is None:
return None
odd = head
even = head.next
even_head = head.next
# 반복하면서 홀짝 노드 처리
while even and even.next:
odd.next, even.next = odd.next.next, even.next.next
odd, even = odd.next, even.next
# 홀수 노드의 마지막을 짝수 헤드로 연결
odd.next = even_head
return head
Result
Runtime : 44ms, Memory : 16.2MB
문제07 역순 연결 리스트 II
https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii
인덱스 m에서 n까지를 역순으로 만들어라. 인덱스 m은 1부터 시작한다.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4 Output: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
- 풀이1_반복 구조로 노드 뒤집기
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, m: int, n: int) -> ListNode:
# 예외 처리
if not head or m==n:
return head
root = start = ListNode(None)
root.next = head
# start, end 지정
for _ in range(m-1):
start = start.next
end = start.next
# 반복하면서 노드 차례대로 뒤집기
for _ in range(n-m):
tmp, start.next, end.next = start.next, end.next, end.next.next
start.next.next = tmp
return root.nextㄴ
Result
Runtime : 32ms, Memory : 14.3MB