파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰_그래프
«파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰 서적 내용을 정리»
문제01 섬의 개수
https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-islands
1을 육지로, 0을 물로 가정한 2D 그리드 맵이 주어졌을 때, 섬의 개수를 계산하라.
(연결되어 있는 1의 덩어리 개수를 구하라.)
섬은 물로 둘러싸여 있으며 격자의 네 모서리가 모두 물로 둘러싸여 있다.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [ ["1","1","1","1","0"], ["1","1","0","1","0"], ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["0","0","0","0","0"] ] Output: 1Example 2:
Input: grid = [ ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["0","0","1","0","0"], ["0","0","0","1","1"] ] Output: 3
- 풀이1_DFS로 그래프 탐색
class Solution:
def numIslands(self, grid: List[List[str]]) -> int:
def dfs(i, j):
# 더 이상 땅이 아닌 경우 종료
if i < 0 or i >= len(grid) or \
j < 0 or j >= len(grid[0]) or \
grid[i][j] != '1':
return
grid[i][j] = 0
# 동서남북 탐색
dfs(i+1, j)
dfs(i-1, j)
dfs(i, j+1)
dfs(i, j-1)
count = 0
for i in range(len(grid)):
for j in range(len(grid[0])):
if grid[i][j] == '1':
dfs(i, j)
# 모든 육지 탐색 후 카운트 1 증가
count += 1
return count
Result
Runtime : 224ms, Memory : 15.5MB
- grid가 아래와 같은 경우 그림으로 확인하는 알고리즘
grid = [ [“1”,”1”,”0”], [“1”,”1”,”0”], [“0”,”0”,”0”] ]
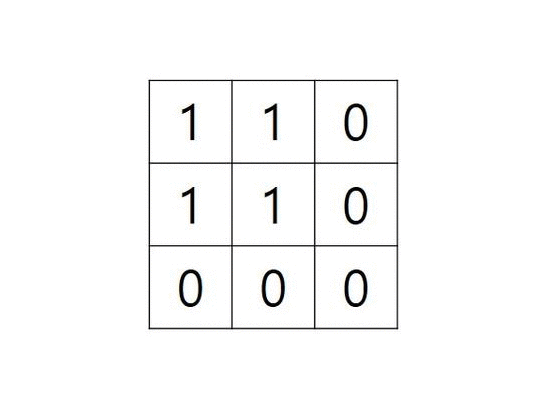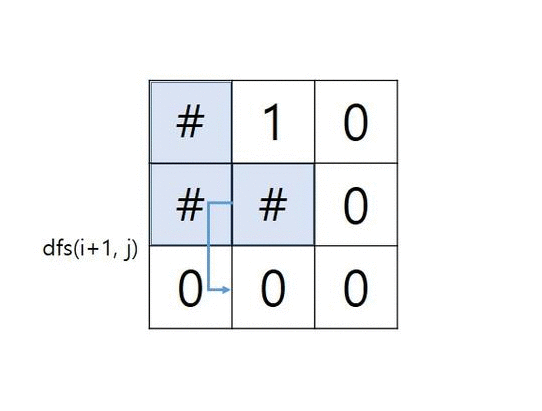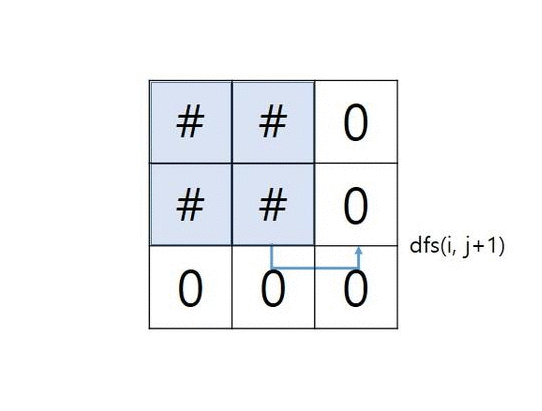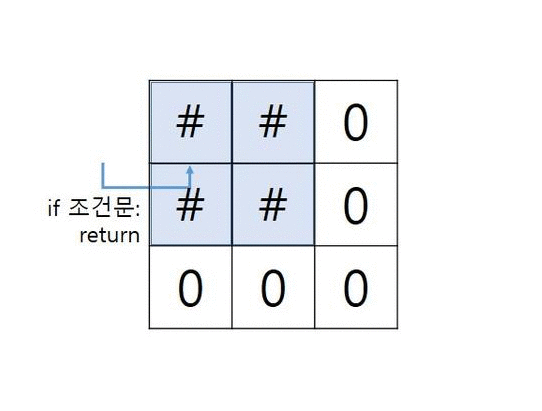
중첩 함수
중첩 함수란 함수 내에 위치한 또 다흔 함수로, 바깥에 위치한 함수들과 달리 부모 함수의 변수를 자유롭게 읽을 수 있다는 장점이 있다.
def outer_function(t: str):
text : str = t
def inner_function():
print(text)
inner_function()
outer_function('Hello!')
# Hello!
#outer_function()은 inner_function()을 호출했고, 아무런 파라미터도 넘기지 않았지만 부모 함수의 text 변수를 자유롭게 읽어들여 그 값인 Hello!를 출력했다.
문제02 전화 번호 문자 조합
https://leetcode.com/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number
2에서 9까지 숫자가 주어졌을 때 전화 번호로 조합 가능한 모든 문자를 출력하라.
Example 1:
Input: digits = "23" Output: ["ad","ae","af","bd","be","bf","cd","ce","cf"]Example 2:
Input: digits = "" Output: []Example 3:
Input: digits = "2" Output: ["a","b","c"]
- 풀이1_모든 조합 탐색
class Solution:
def letterCombinations(self, digits: str) -> List[str]:
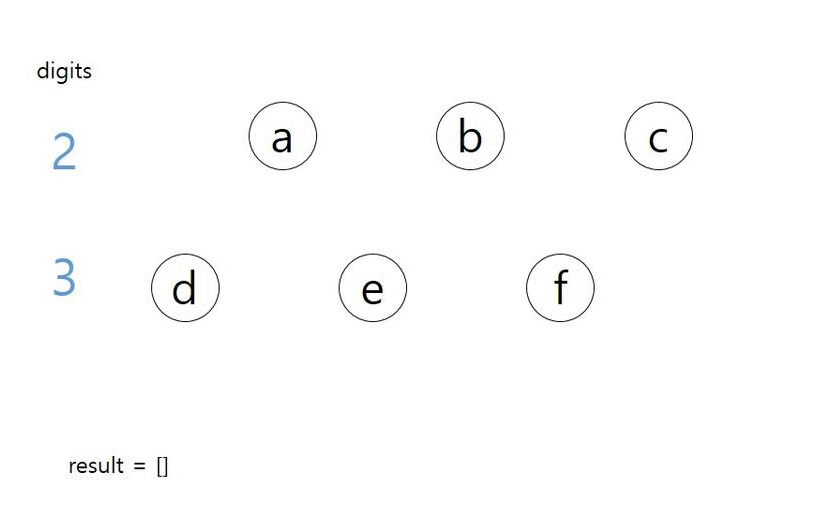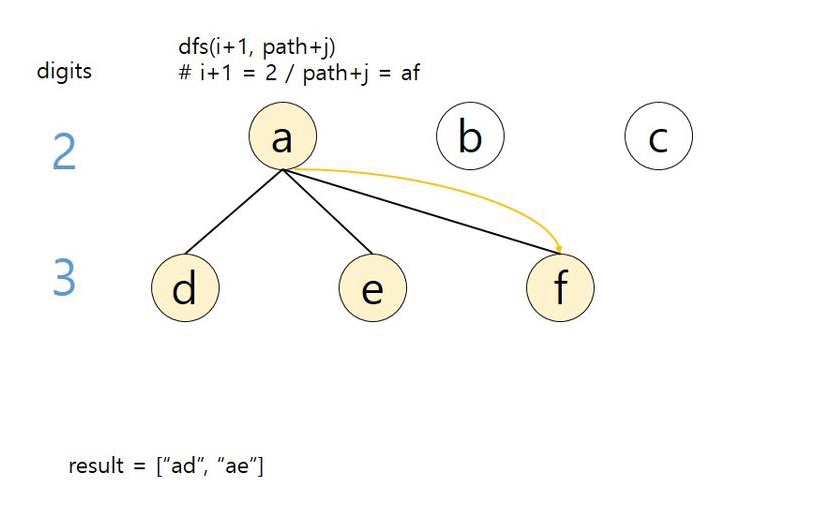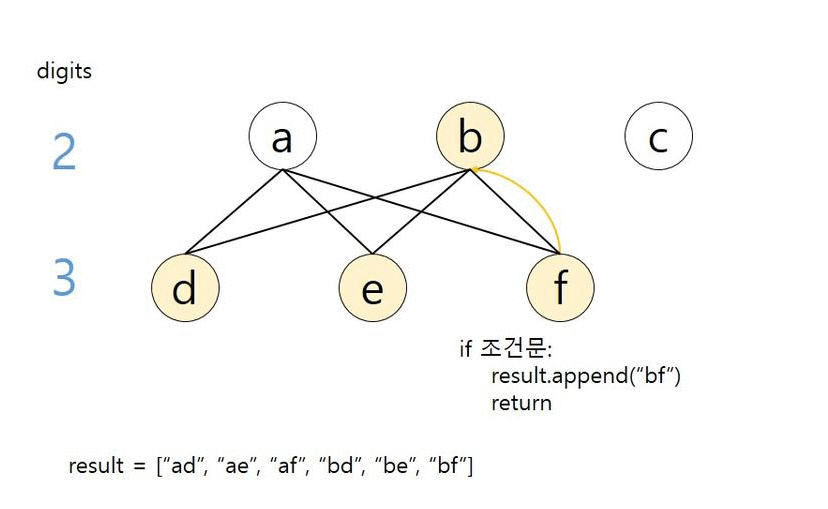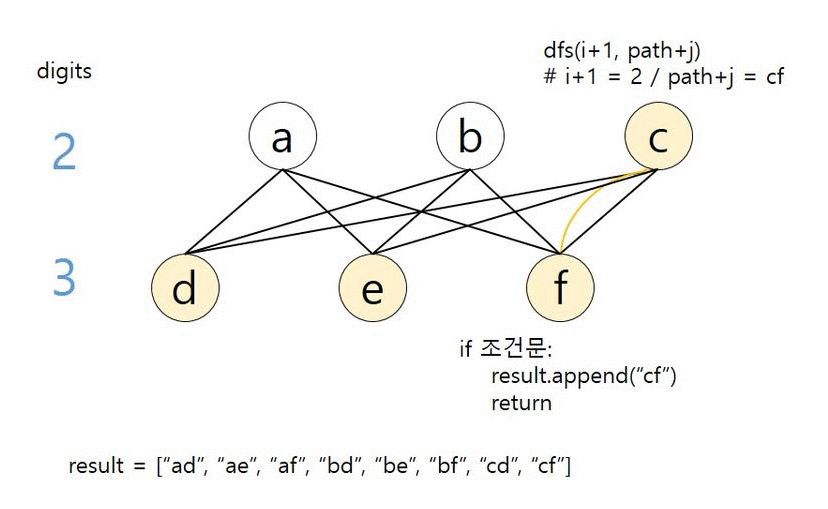
def dfs(index, path):
# 끝까지 탐색하면 백트래킹
if len(path) == len(digits):
result.append(path)
return
# 입력값 자릿수 단위 반복
for i in range(index, len(digits)):
# 숫자에 해당하는 모든 문자열 반복
for j in dic[digits[i]]:
dfs(i+1, path+j)
# 예외처리
if not digits:
return []
dic = {"2": "abc", "3": "def", "4": "ghi", "5": "jkl",
"6": "mno", "7": "pqrs", "8": "tuv", "9": "wxyz"}
result = []
dfs(0, "")
return result
Result
Runtime : 48ms, Memory : 14.4MB
문제03 순열
https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations
서로 다른 정수를 입력받아 가능한 모든 순열을 리턴하라.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,1] Output: [[0,1],[1,0]]Example 3:
Input: nums = [1] Output: [[1]]
- 풀이1_DFS를 활용한 순열 생성
class Solution:
def permute(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
results = []
prev_elements = []
def dfs(elements):
# 리프 노드일 때 결과 추가
if len(elements) == 0:
results.append(prev_elements[:])
# 순열 생성 재귀 호출
for e in elements:
next_elements = elements[:]
next_elements.remove(e)
prev_elements.append(e)
dfs(next_elements)
prev_elements.pop()
dfs(nums)
return results
Result
Runtime : 64ms, Memory : 14.4MB
- 풀이2_itertools 모듈 사용
class Solution:
def permute(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
return list(itertools.permutations(nums))
Result
Runtime : 44ms, Memory : 14.3MB
객체 복사
파이썬의 중요한 특징 중 하나가 모든 것이 객체라는 점이다. 그러다 보니 별도로 값을 복사하지 않는 한, 변수에 값을 할당하는 모든 행위는 값 객체에 대한 참조가 된다.
그렇다면 참조가 되지 않도록 값 자체를 복사하려면 어떻게 해야할까?
# 1) [:]로 처리하는 방법
a = [1, 2, 3]
b = a
c = a[:]
print(id(a), id(b), id(c))
# 2907685897672 2907685897672 2907685897864
# 2) copy()메소드를 사용하는 방법
d = a.copy()
print(id(a), id(b), id(c), id(d))
# 2907685897672 2907685897672 2907685897864 2907685887880
# 3) 복잡한 리스트는 copy.deepcopy()로 처리
import copy
a = [1, 2, [3, 5], 4]
b = copy.deepcopy(a)
print(id(a), id(b), b)
# 2907685928328 2907685928136 [1, 2, [3, 5], 4]
문제04 조합
https://leetcode.com/problems/combinations
전체 수n을 입력받아 k개의 조합(combination)을 리턴하라.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4, k = 2 Output: [ [2,4], [3,4], [2,3], [1,2], [1,3], [1,4], ]Example 2:
Input: n = 1, k = 1 Output: [[1]]
- 풀이1_DFS로 k개 조합 생성
class Solution:
def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
results = []
def dfs(elements, start: int, k: int):
if k == 0:
results.append(elements[:])
return
# 자신 이전의 모든 값을 고정하여 재귀 호출
for i in range(start, n + 1):
elements.append(i)
dfs(elements, i + 1, k - 1)
elements.pop()
dfs([], 1, k)
return results
Result
Runtime : 428ms, Memory : 15.8MB
- 풀이2_itertools 모듈 사용
class Solution:
def combine(self, n: int, k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
return list(itertools.combinations(range(1, n + 1), k))
Result
Runtime : 92ms, Memory : 15.6MB
순열과 조합
문제05 조합의 합
https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum
숫자 집합candidates를 조합하여 합이 target이 되는 원소를 나열하라. 각 원소는 중복으로 나열 가능하다.
Example 1:
Input: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7 Output: [[2,2,3],[7]] Explanation: 2 and 3 are candidates, and 2 + 2 + 3 = 7. Note that 2 can be used multiple times. 7 is a candidate, and 7 = 7. These are the only two combinations.Example 2:
Input: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8 Output: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]Example 3:
Input: candidates = [2], target = 1 Output: []Example 4:
Input: candidates = [1], target = 1 Output: [[1]]Example 5:
Input: candidates = [1], target = 2 Output: [[1,1]]
- 풀이1_DFS로 중복 조합 그래프 탐색
class Solution:
def combinationSum(candidates, target):
result = []
# csum : 합을 갱신해 나갈 파라미터, index : 순서 파라미터, path : 지금까지의 탐색 경로
def dfs(csum, index, path):
# 종료 조건
if csum < 0: # 목표값을 초과한 경우로 탐색을 종료
return
if csum == 0: # csum이 target값과 일치하는 정답이므로 결과 리스트에 추가하고 탐색을 종료
result.append(path)
return
# 자신 부터 하위 원소 까지의 나열 재귀 호출
for i in range(index, len(candidates)):
dfs(csum - candidates[i], i, path + [candidates[i]])
# 만약 문제가 순열이라면, dfs(csum - candidates[i], 0, path + [candidates[i]]) i를 0부터 시작해 첫번째 값부터 탐색하면 됨.
dfs(target, 0, [])
return result
Result
Runtime : 76ms, Memory : 14.3MB
문제06 부분 집합
https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets
모든 부분 집합을 리턴하라.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: [[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]Example 2:
Input: nums = [0] Output: [[],[0]]
- 풀이1_트리의 모든 DFS 결과
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
result = []
def dfs(index, path):
# 매번 결과 추가
result.append(path)
# 경로를 만들면서 DFS
for i in range(index, len(nums)):
dfs(i+1, path + [nums[i]])
dfs(0, [])
return result
Result
Runtime : 36ms, Memory : 14.4MB
문제07 일정 재구성
https://leetcode.com/problems/reconstruct-itinerary
[from, to]로 구성된 항공권 목록을 이용해 JFK에서 출발하는 여행 일정을 구성하라.
여러 일정이 있는 경우 사전 어휘 순으로 방문한다.
Example 1:
Input: [["MUC", "LHR"], ["JFK", "MUC"], ["SFO", "SJC"], ["LHR", "SFO"]] Output: ["JFK", "MUC", "LHR", "SFO", "SJC"]Example 2:
Input: [["JFK","SFO"],["JFK","ATL"],["SFO","ATL"],["ATL","JFK"],["ATL","SFO"]] Output: ["JFK","ATL","JFK","SFO","ATL","SFO"] Explanation: Another possible reconstruction is ["JFK","SFO","ATL","JFK","ATL","SFO"]. But it is larger in lexical order.
- 풀이1_DFS로 일정 그래프 구성
class Solution:
def findItinerary(self, tickets: List[List[str]]) -> List[str]:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
# 그래프 순서대로 구성
for a, b in sorted(tickets):
graph[a].append(b)
# defaultdict(<class 'list'>, {'ATL': ['JFK', 'SFO'], 'JFK': ['ATL', 'SFO'], 'SFO': ['ATL']})
route = []
def dfs(a):
# 첫 번째 값을 읽어 어휘 순 방문
while graph[a]:
dfs(graph[a].pop(0))
route.append(a)
dfs('JFK')
# 다시 뒤집어 어휘 순 결과로
return route[::-1]
Result
Runtime : 80ms, Memory : 14.8MB
- 풀이2_스택 연산으로 큐 연상 최적화 시도
class Solution:
def findItinerary(self, tickets: List[List[str]]) -> List[str]:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
# 그래프를 뒤집어서 구성
for a, b in sorted(tickets, reverse=True):
graph[a].append(b)
# defaultdict(<class 'list'>, {'SFO': ['ATL'], 'JFK': ['SFO', 'ATL'], 'ATL': ['SFO', 'JFK']})
route = []
def dfs(a):
# 마지막 값을 읽어 어휘 순 방문
while graph[a]:
dfs(graph[a].pop())
route.append(a)
dfs('JFK')
# 다시 뒤집어 어휘 순 결과로
return route[::-1]
Result
Runtime : 76ms, Memory : 14.9MB
- 풀이3_일정 그래프 반복
class Solution:
def findItinerary(self, tickets: List[List[str]]) -> List[str]:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
# 그래프 순서대로 구성
for a, b in sorted(tickets):
graph[a].append(b)
route, stack = [], ['JFK']
while stack :
# 반복으로 스택을 구성하되 막히는 부분에서 풀어내는 처리
while graph[stack[-1]]:
stack.append(graph[stack[-1]].pop(0))
route.append(stack.pop())
# 다시 뒤집어서 어휘 순 결과로
return route[::-1]
Result
Runtime : 72ms, Memory : 14.6MB
문제08 코스 스케줄
https://leetcode.com/problems/course-schedule
0을 완료하기 위해서는 1을 끝내야 한다는 것을 [0,1] 쌍으로 표현하는 n개의 코스가 있다. 코스 개수 n과 이 쌍들을 입력으로 받았을 때 모든 코스가 완료 가능한지 판별하라.
Example 1:
Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]] Output: true Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So it is possible.Example 2:
Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0],[0,1]] Output: false Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0, and to take course 0 you should also have finished course 1. So it is impossible.
- 풀이1_DFS로 순환 구조 판별
class Solution:
def canFinish(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
# 그래프 구성
for x, y in prerequisites:
graph[x].append(y)
traced = set()
def dfs(i):
# 순환 구조이면 False
if i in traced:
return False
traced.add(i)
for y in graph[i]:
if not dfs(y):
return False
# 탐색 종료 후 순환 노드 삭제
traced.remove(i)
return True
# 순환 구조 판별
for x in list(graph):
if not dfs(x):
return False
return True
Result
Time Limited Exeeceded
- 풀이2_가지치기를 이용한 최적화
class Solution:
def canFinish(self, numCourses: int, prerequisites: List[List[int]]) -> bool:
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
# 그래프 구성
for x, y in prerequisites:
graph[x].append(y)
traced = set()
visited = set()
def dfs(i):
# 순환 구조이면 False
if i in traced:
return False
# 이미 방문했던 노드이면 True
if i in visited:
return True
traced.add(i)
for y in graph[i]:
if not dfs(y):
return False
# 탐색 종료 후 순환 노드 삭제
traced.remove(i)
# 탐색 종료 후 방문 노드 추가
visited.add(i)
return True
# 순환 구조 판별
for x in list(graph):
if not dfs(x):
return False
return True
Result
Runtime : 100ms, Memory : 17.9MB