파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰_이진 트리
«파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰 서적 내용을 정리»
- 문제01 이진 트리의 최대 깊이
- 문제02 이진 트리의 직경
- 문제03 가장 긴 동일 값의 경로
- 문제04 이진 트리 반전
- 문제05 두 이진 트리 병합
- 문제06 이진 트리 직렬화 & 역직렬화
- 문제07 균형 이진 트리
- 문제08 최소 높이 트리
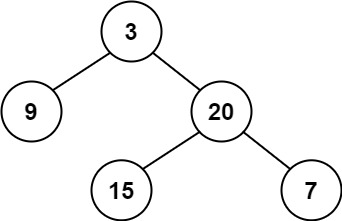
문제01 이진 트리의 최대 깊이
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree
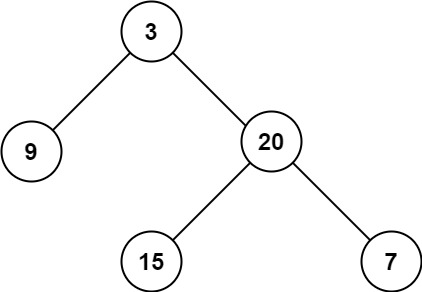
이진 트리의 최대 깊이를 구하라.
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 3Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: 2Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: 0Example 4:
Input: root = [0] Output: 1
- 풀이1_반복 구조로 BFS 풀이
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
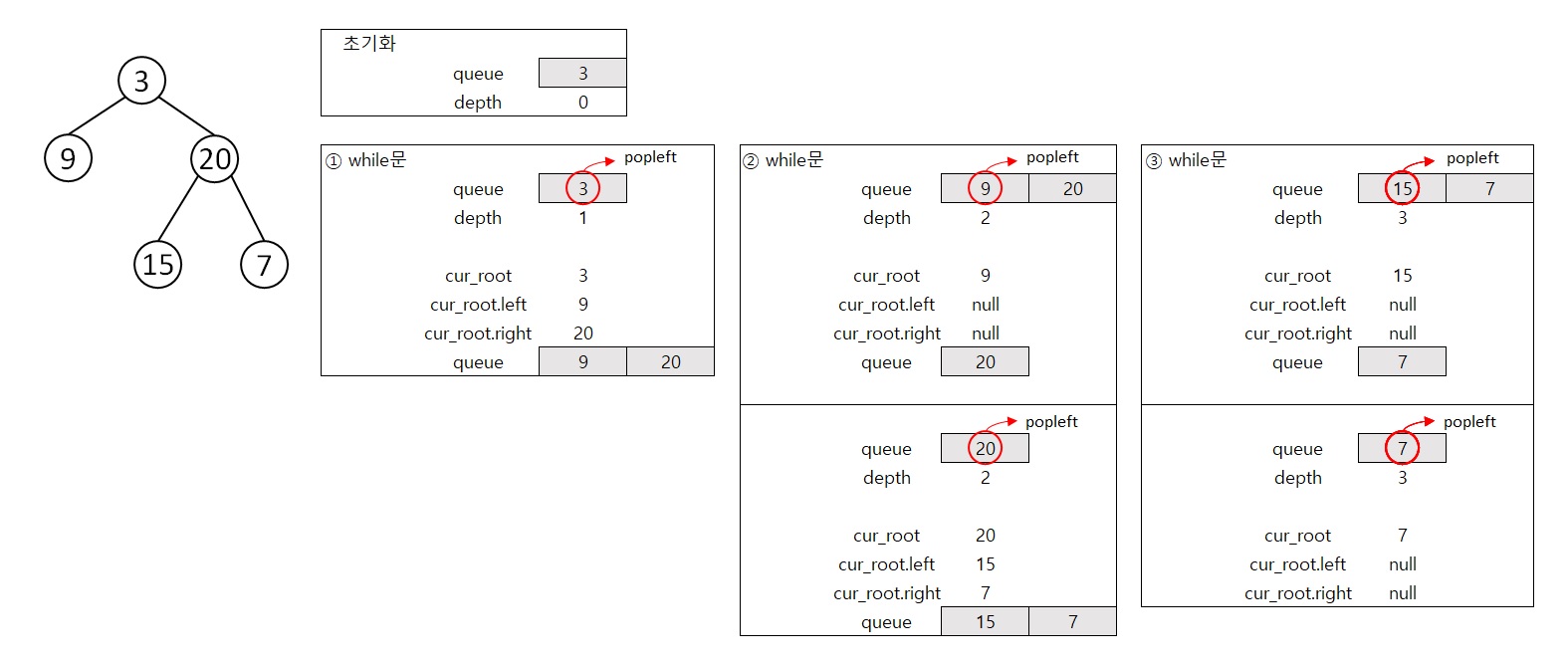
queue = collections.deque([root])
depth = 0
while queue:
depth += 1
# 큐 연산 추출 노드의 자식 노드 삽입
for _ in range(len(queue)):
cur_root = queue.popleft()
if cur_root.left:
queue.append(cur_root.left)
if cur_root.right:
queue.append(cur_root.right)
# BFS 반복 횟수 == 깊이
return depth
Result
Runtime : 32ms, Memory : 15.3MB
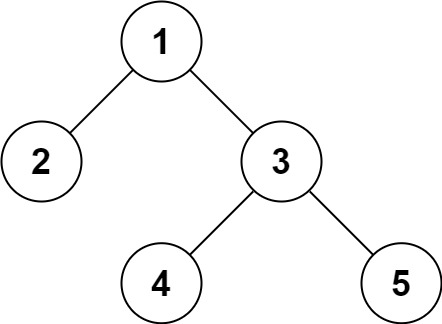
문제02 이진 트리의 직경
https://leetcode.com/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree
이진 트리에서 두 노드 간 긴 경로의 길이를 출력하라.
Example: Given a binary tree
1 / \ 2 3 / \ 4 5Return 3, which is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
- 풀이1_상태값 누적 트리 DFS
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
longest : int = 0
def diameterOfBinaryTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
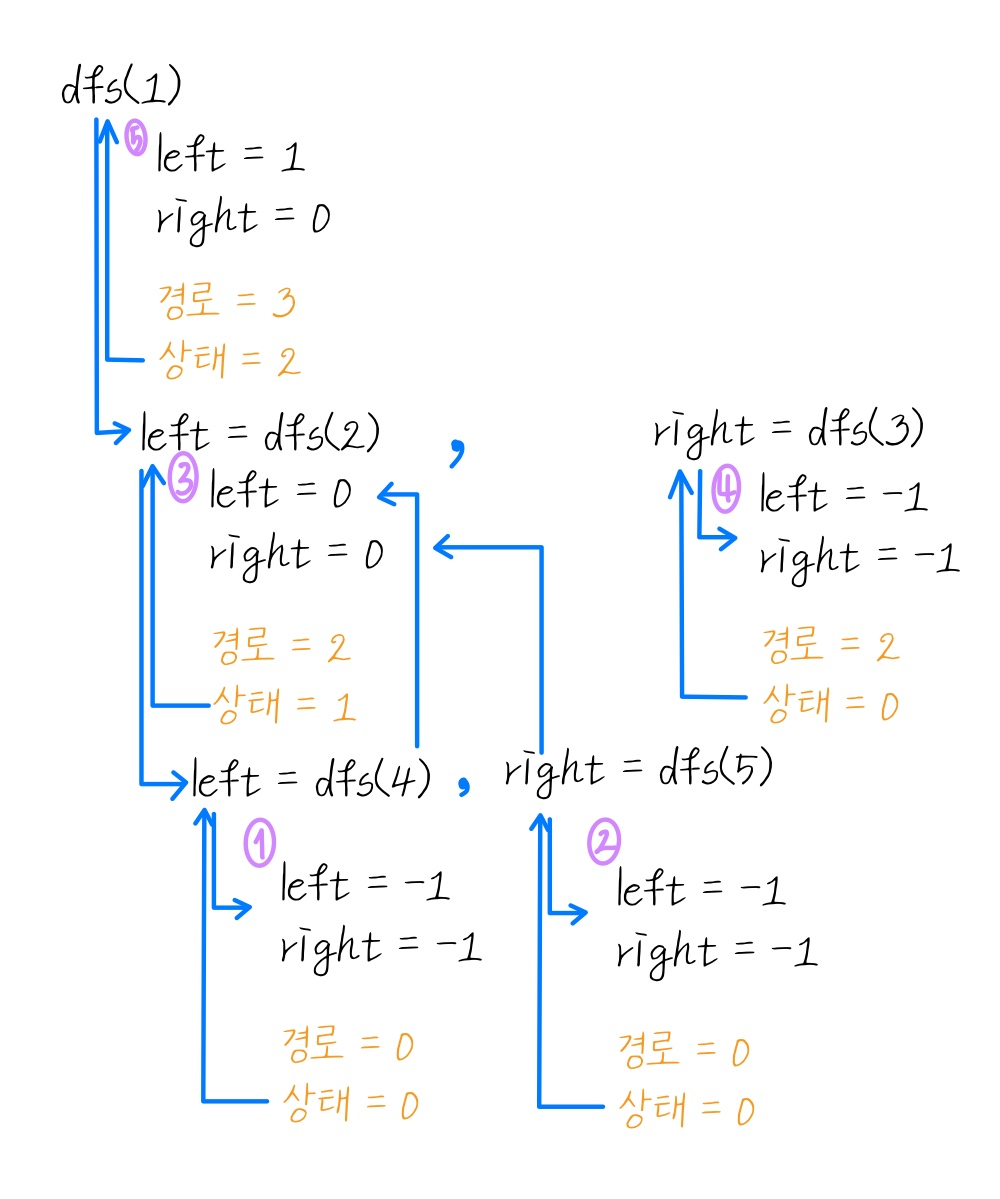
def dfs(node: TreeNode) -> int:
if not node:
return -1
# 왼쪽, 오른쪽 각 리프 노드까지 탐색
left = dfs(node.left)
right = dfs(node.right)
# 가장 긴 경로
self.longest = max(self.longest, left + right + 2)
# 상태값
return max(left, right) + 1
dfs(root)
return self.longest
Result
Runtime : 36ms, Memory : 16.4MB
문제03 가장 긴 동일 값의 경로
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-univalue-path
동일한 값을 지닌 가장 긴 경로를 찾아라.
Example 1:
Input: root = [5,4,5,1,1,5] Output: 2Example 2:
Input: root = [1,4,5,4,4,5] Output: 2
- 풀이1_상태값 거리 계산 DFS
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
result: int = 0
def longestUnivaluePath(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
def dfs(node: TreeNode):
if node is None:
return -1
# 존재하지 않는 노드까지 DFS 재귀 탐색
left = dfs(node.left)
right = dfs(node.right)
# 현재 노드가 자식 노드와 동일한 경우 거리 1 증가
if node.left and node.left.val == node.val:
left += 1
else:
left = 0
if node.right and node.right.val == node.val:
right += 1
else:
right = 0
# 왼쪽과 오른쪽 자식 노드 간 거리의 합 최댓값이 결과
self.result = max(self.result, left + right)
# 자식 노드 상태값 둥 큰 값 리턴
return max(left, right)
dfs(root)
return self.result
Result
Runtime : 392ms, Memory : 17.9MB
문제04 이진 트리 반전
https://leetcode.com/problems/invert-binary-tree
이진 트리를 반전시켜라.
Example:
Input:
4 / \ 2 7 / \ / \ 1 3 6 9Output:
4 / \ 7 2 / \ / \ 9 6 3 1
- 풀이1_파이썬다운 방식
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if root:
root.left, root.right = self.invertTree(root.right), self.invertTree(root.left)
return root
return None # 생략가능
Result
Runtime : 32ms, Memory : 14.3MB
- 풀이2_반복 구조로 BFS
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
queue = collections.deque([root])
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
# 부모 노드부터 하향식 스왑
if node:
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left
queue.append(node.left)
queue.append(node.right)
return root
Result
Runtime : 28ms, Memory : 14.3MB
- 풀이3_반복 구조로 DFS
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
stack = collections.deque([root])
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
# 부모 노드 부터 하향식 스왑
if node:
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left
stack.append(node.left)
stack.append(node.right)
return root
Result
Runtime : 20ms, Memory : 14.1MB
- 풀이4_반복 구조로 DFS 후위 순회
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def invertTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
stack = collections.deque([root])
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node:
stack.append(node.left)
stack.append(node.right)
node.left, node.right = node.right, node.left # 후위 순회
return root
Result
Runtime : 32ms, Memory : 14.2MB
문제05 두 이진 트리 병합
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-binary-trees
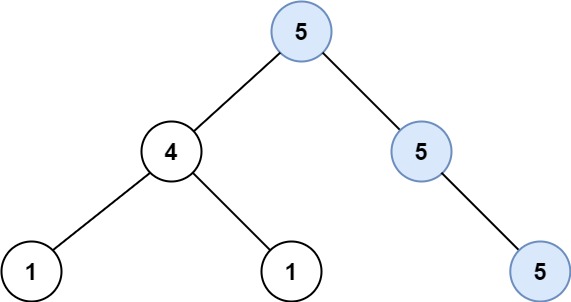
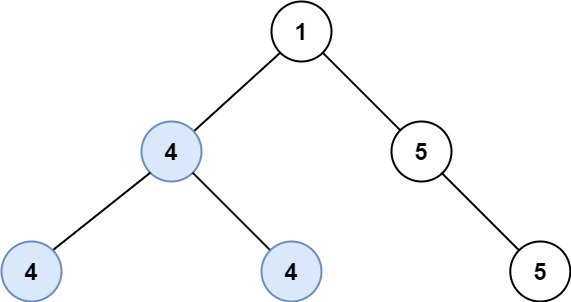
두 이진 트리를 병합하라. 중복되는 노드는 값을 합산한다.
Example 1:
Input: root1 = [1,3,2,5], root2 = [2,1,3,null,4,null,7] Output: [3,4,5,5,4,null,7]Example 2:
Input: root1 = [1], root2 = [1,2] Output: [2,2]
- 풀이1_재귀 탐색
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def mergeTrees(self, root1: TreeNode, root2: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
if root1 and root2:
node = TreeNode(root1.val + root2.val)
node.left = self.mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left)
node.right = self.mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right)
return node
else:
return root1 or root2
Result
Runtime : 72ms, Memory : 15.3MB
문제06 이진 트리 직렬화 & 역직렬화
https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree
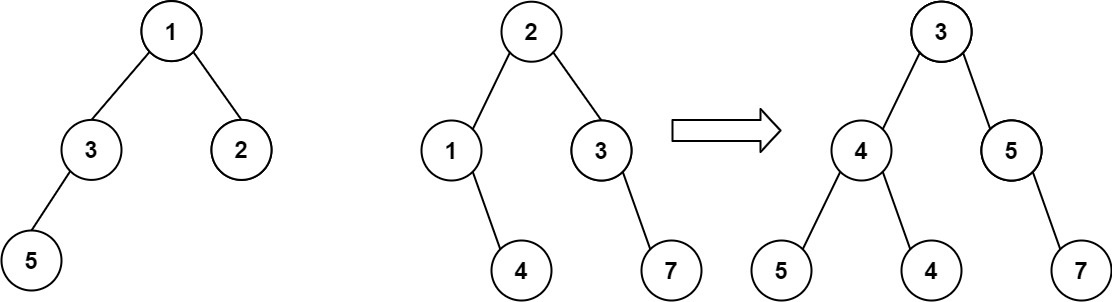
이진 트리를 배열로 직렬화하고, 반대로 역직렬화하는 기능을 구현하라. 즉 다음과 같은 트리는 [1, 2, 3, null, null, 4, 5] 형태로 직렬화할 수 있을 것이다.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5] Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []Example 3:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1]Example 4:
Input: root = [1,2] Output: [1,2]
- 풀이1_직렬화 & 역직렬화 구현
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Codec:
# 직렬화
def serialize(self, root):
"""Encodes a tree to a single string.
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: str
"""
queue = collections.deque([root])
result =['#']
# 트리 BFS 직렬화
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if node:
queue.append(node.left)
queue.append(node.right)
result.append(str(node.val))
else:
result.append('#')
return ' '.join(result)
# 역직렬화
def deserialize(self, data):
"""Decodes your encoded data to tree.
:type data: str
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
# 예외 처리
if data == '# #':
return None
nodes = data.split()
root = TreeNode(int(nodes[1]))
queue = collections.deque([root])
index = 2
# 빠른 런너처럼 자식 노드 결과를 먼저 확인 후 큐 삽입
while queue:
node = queue.popleft()
if nodes[index] is not '#':
node.left = TreeNode(int(nodes[index]))
queue.append(node.left)
index += 1
if nodes[index] is not '#':
node.right = TreeNode(int(nodes[index]))
queue.append(node.right)
index += 1
return root
# Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
# ser = Codec()
# deser = Codec()
# ans = deser.deserialize(ser.serialize(root))
Result
Runtime : 112ms, Memory : 18.8MB
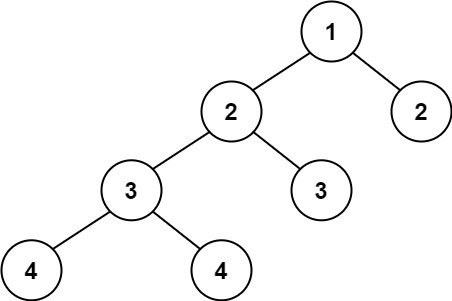
문제07 균형 이진 트리
https://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree
이진 트리가 높이 균형(Height-Balanced)인지 판단하라.
높이 균형은 모든 노드의 서브 트리 간의 높이 차이가 1 이하인 것을 말한다.
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: trueExample 2:
Input: root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4] Output: falseExample 3:
Input: root = [] Output: true
- 풀이1_재귀 구조로 높이 차이 계산
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
def check(root):
if not root:
return 0
left = check(root.left)
right = check(root.right)
# 높이 차이가 나는 경우 -1, 이외에는 높이에 따라 1 증가
if left == -1 or right == -1 or abs(left - right) > 1:
return -1
return max(left, right) + 1
return check(root) != -1
Result
Runtime : 36ms, Memory : 19MB
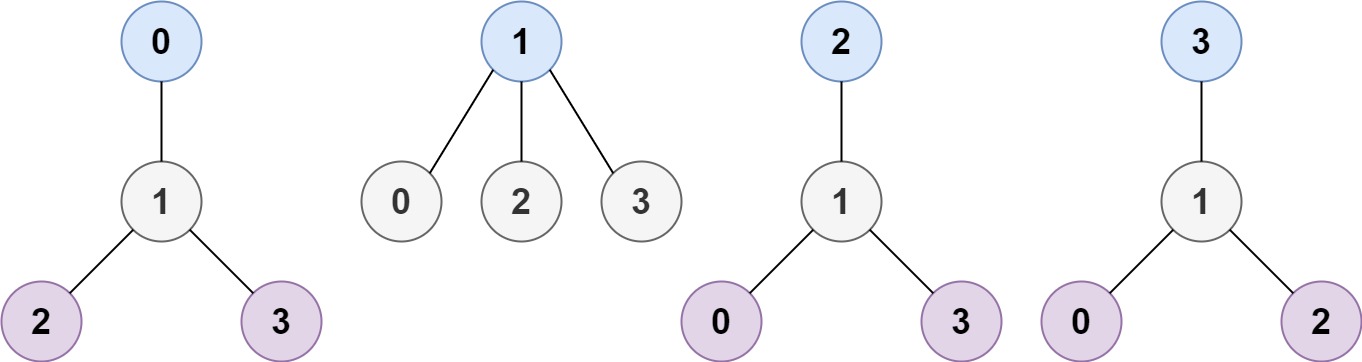
문제08 최소 높이 트리
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-height-trees
노드 개수와 무방향 그래프를 입력받아 트리가 최소 높이가 되는 루트의 목록을 리턴하라.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,0],[1,2],[1,3]] Output: [1] Explanation: As shown, the height of the tree is 1 when the root is the node with label 1 which is the only MHT.Example 2:
Input: n = 6, edges = [[3,0],[3,1],[3,2],[3,4],[5,4]] Output: [3,4]Example 3:
Input: n = 1, edges = [] Output: [0]Example 4:
Input: n = 2, edges = [[0,1]] Output: [0,1]
- 풀이1_단계별 리프 노드 제거
class Solution:
def findMinHeightTrees(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
if n <= 1:
return [0]
# 양방향 그래프 구성(무방향 그래프이기 때문에)
graph = collections.defaultdict(list)
for i, j in edges:
graph[i].append(j)
graph[j].append(i)
# defaultdict(<class 'list'>, {1: [0, 2, 3], 0: [1], 2: [1], 3: [1]})
# 첫 번째 리프 노드 leaves에 추가
# 리프 노드 = 해당 키의 값이 1개 뿐인 것
leaves = []
for i in range(n+1):
if len(graph[i]) == 1:
leaves.append(i)
# leaves = [0, 2, 3]
# 루트 노드만 남을 때까지 반복 제거
while n > 2:
n -= len(leaves)
new_leaves = []
for leaf in leaves:
neighbor = graph[leaf].pop()
graph[neighbor].remove(leaf)
if len(graph[neighbor]) == 1:
new_leaves.append(neighbor)
leaves = new_leaves
return leaves
Result
Runtime : 224ms, Memory : 18.2MB