파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰_이진 트리
«파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰 서적 내용을 정리»
- 문제01 정렬된 배열의 이진 탐색 트리 변환
- 문제02 이진 탐색 트리(BST)를 더 큰 수 합계 트리로
- 문제03 이진 탐색 트리(BST) 합의 범위
- 문제04 이진 탐색 트리(BST) 노드 간 최소 거리
- 문제05 전위, 중위 순회 결과로 이진 트리 구축
문제01 정렬된 배열의 이진 탐색 트리 변환
https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree
오름차순으로 정렬된 배열을 높이 균형 이진 탐색 트리로 변환하라.
Example:
Given the sorted array: [-10,-3,0,5,9], One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST: 0 / \ -3 9 / / -10 5
- 풀이1_이진 검색 결과로 트리 구성
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
if not nums:
return None
mid = len(nums) // 2
# 분할 정복으로 이진 검색 결과 트리 구성
node = TreeNode(nums[mid])
node.left = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[:mid])
node.right = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[mid + 1 :])
return node
Result
Runtime : 76ms, Memory : 16.6MB
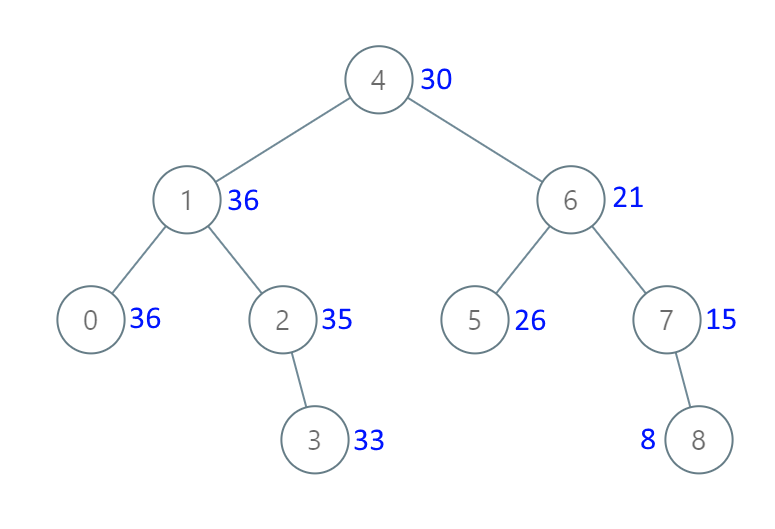
문제02 이진 탐색 트리(BST)를 더 큰 수 합계 트리로
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree
BST의 각 노드를 현재값보다 더 큰 값을 가진 모든 노드의 합으로 만들어라.
Example 1:
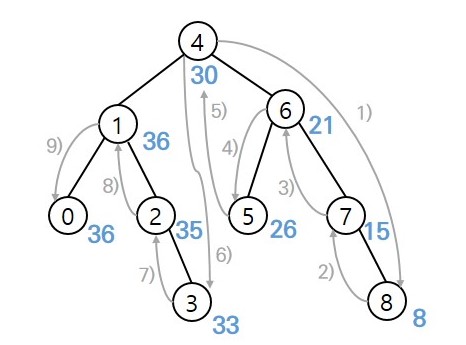
Input: root = [4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8] Output: [30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]Example 2:
Input: root = [0,null,1] Output: [1,null,1]Example 3:
Input: root = [1,0,2] Output: [3,3,2]Example 4:
Input: root = [3,2,4,1] Output: [7,9,4,10]
- 풀이1_중위 순회로 노드 값 누적
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
val : int = 0
def bstToGst(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:
# 중위 순회 노드 값 누적
if root:
self.bstToGst(root.right)
self.val += root.val
root.val = self.val
self.bstToGst(root.left)
return root
Result
Runtime : 32ms, Memory : 14.3MB
문제03 이진 탐색 트리(BST) 합의 범위
https://leetcode.com/problems/range-sum-of-bst
이진 탐색 트리(BST)가 주어졌을 때 L 이상 R 이하의 값을 지닌 노드의 합을 구하라.
Example 1:
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15 Output: 32Example 2:
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10 Output: 23
- 풀이1_재귀 구조 DFS로 브루트 포스 탐색
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: TreeNode, low: int, high: int) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
return (root.val if low <= root.val <= high else 0) + \
self.rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high) + \
self.rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high)
Result
Runtime : 272ms, Memory : 22.3MB
- 풀이2_DFS 가지치기로 필요한 노드 탐색
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: TreeNode, low: int, high: int) -> int:
def dfs(node: TreeNode):
if not node:
return 0
# 루트가 low보다 작은 경우, 왼쪽 서브 트리 가지치기
if node.val < low:
return dfs(node.right)
# 루트가 high보다 큰 경우, 오른쪽 서브 트리 가지치기
elif node.val > high:
return dfs(node.left)
# low <= root.val <= high인 경우
return node.val + dfs(node.left) + dfs(node.right)
return dfs(root)
Result
Runtime : 188ms, Memory : 22.3MB
- 풀이3_반복 구조 DFS로 필요한 노드 탐색
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: TreeNode, low: int, high: int) -> int:
stack, sum = [root], 0
# 스택 이용 필요한 노드 DFS 반복
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node:
if node.val > low:
stack.append(node.left)
if node.val < high:
stack.append(node.right)
if low <= node.val <= high:
sum += node.val
return sum
Result
Runtime : 192ms, Memory : 22.1MB
- 풀이4_반복 구조 BFS로 필요한 노드 탐색
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: TreeNode, low: int, high: int) -> int:
stack, sum = [root], 0
# 스택 이용 필요한 노드 DFS 반복
while stack:
node = stack.pop(0)
if node:
if node.val > low:
stack.append(node.left)
if node.val < high:
stack.append(node.right)
if low <= node.val <= high:
sum += node.val
return sum
Result
Runtime : 208ms, Memory : 22MB
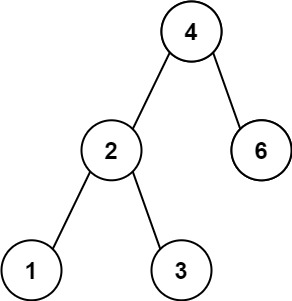
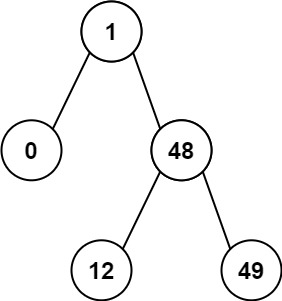
문제04 이진 탐색 트리(BST) 노드 간 최소 거리
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-distance-between-bst-nodes
두 노드 간 값의 차이가 가장 작은 노드의 값의 차이를 출력하라.
Example 1:
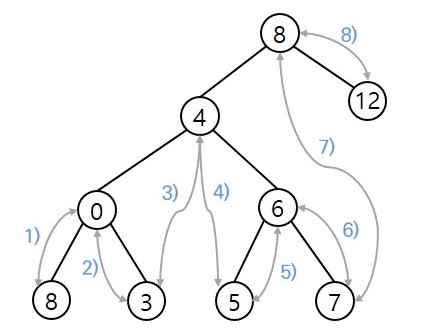
Input: root = [4,2,6,1,3] Output: 1Example 2:
Input: root = [1,0,48,null,null,12,49] Output: 1
- root와 가장 가까운 거리에 있는 노드는 왼쪽 서브 트리에서 가장 큰 값, 오른쪽 서브 트리에서 가장 작은 값이다.
- 풀이1_재귀 구조로 중위 순회
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
prev = -sys.maxsize
result = sys.maxsize
# 재귀 구조 중위 순회 비교 결과
def minDiffInBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if root.left:
self.minDiffInBST(root.left)
self.result = min(self.result, root.val - self.prev)
self.prev = root.val
if root.right:
self.minDiffInBST(root.right)
return self.result
Result
Runtime : 28ms, Memory : 14.3MB
- 풀이2_반복 구조로 중위 순회
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDiffInBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
prev = -sys.maxsize
result = sys.maxsize
stack = []
node = root
# 반복 구조 중위 순회 비교 결과
while stack or node:
while node:
stack.append(node)
node = node.left
node = stack.pop()
result = min(result, node.val - prev)
prev = node.val
node = node.right
return result
Result
Runtime : 32ms, Memory : 14.2MB
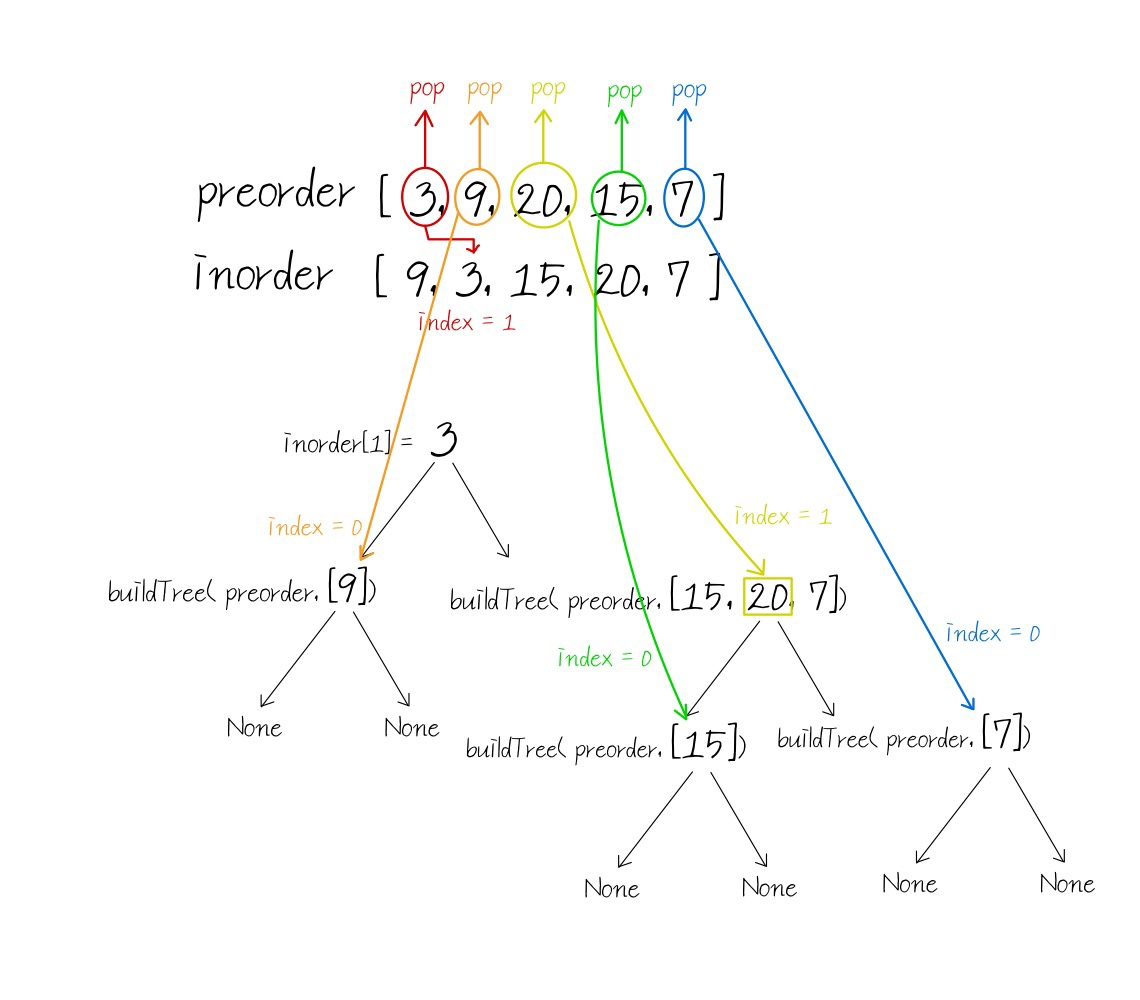
문제05 전위, 중위 순회 결과로 이진 트리 구축
https://leetcode.com/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal
트리의 전위, 중위 순회 결과를 입력값으로 받아 이진 트리를 구축하라.
Example
preorder = [3,9,20,15,7] inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]Return the following binary tree:
3 / \ 9 20 / \ 15 7
- 풀이1_전위 순회 결과로 중위 순회 분할 정복
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def buildTree(self, preorder: List[int], inorder: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
if inorder:
# 전위 순회 결과는 중위 순회 분할 인덱스
index = inorder.index(preorder.pop(0))
# 중위 순회 결과 분할 정복
node = TreeNode(inorder[index])
node.left = self.buildTree(preorder, inorder[0:index])
node.right = self.buildTree(preorder, inorder[index + 1:])
return node
Result
Runtime : 140ms, Memory : 53.2MB