파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰_정렬
«파이썬 알고리즘 인터뷰 서적 내용을 정리»
문제01 리스트 정렬
https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-list
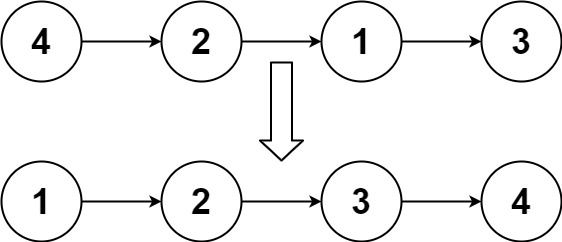
연결 리스트를 O(n log n)에 정렬하라.
Example 1:
Input: head = [4,2,1,3] Output: [1,2,3,4]Example 2:Example 1:
Input: head = [4,2,1,3] Output: [1,2,3,4]Example 2:
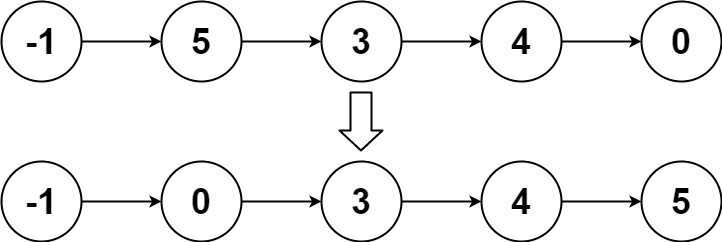
Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0] Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]Example 3:
Input: head = [] Output: []
Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0] Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]Example 3:
Input: head = [] Output: []
- 풀이1_병합 정렬
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1:ListNode, l2:ListNode) -> ListNode:
if l1 and l2:
if l1.val > l2.val:
l1, l2 = l2, l1
l1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2)
return l1 or l2
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not (head and head.next):
return head
# 런너 기법 활용
half, slow, fast = None, head, head
while fast and fast.next:
half, slow, fast = slow, slow.next, fast.next.next
half.next = None
# 분할 재귀 호출
l1 = self.sortList(head)
l2 = self.sortList(slow)
return self.mergeTwoLists(l1, l2)
Result
Runtime : 524ms, Memory : 50.9MB
- 풀이2_내장 함수를 이용하는 실용적인 방법
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# 연결 리스트 -> 파이썬 리스트
p = head
lst: List = []
while p:
lst.append(p.val)
p = p.next
# 정렬
lst.sort()
# 파이썬 리스트 -> 연결 리스트
p = head
for i in range(len(lst)):
p.val = lst[i]
p = p.next
return head
Result
Runtime : 160ms, Memory : 30MB
문제02 구간 병합
https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-intervals
겹치는 구간을 병합하라.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]] Output: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]] Explanation: Since intervals [1,3] and [2,6] overlaps, merge them into [1,6].Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[1,4],[4,5]] Output: [[1,5]] Explanation: Intervals [1,4] and [4,5] are considered overlapping.
- 풀이1_정렬하여 병합
class Solution:
def merge(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
merged = []
for i in sorted(intervals, key=lambda x: x[0]):
if merged and i[0] <= merged[-1][1]:
merged[-1][1] = max(merged[-1][1], i[1])
else:
merged += i,
return merged
Result
Runtime : 88ms, Memory : 16.2MB
콤마(,) 연산자
콤마는 중첩 리스트로 만들어주는 역할을 함
# 기본적인 추가 연산
# 단순히 +=를 했을 때는 요소를 이어붙임.
a = [1]
b = [2, 3]
a += b
print(a)
# [1, 2, 3]
# 콤마(,)연산자 사용
a = [1]
b = [2, 3]
a += b,
print(a)
# [1, [2, 3]]
# []와 동일한 역할
a += [b]
print(a)
# [1, [2, 3]]
문제03 삽입 정렬 리스트
https://leetcode.com/problems/insertion-sort-list
연결 리스트를 삽입 정렬로 정렬하라.
Example 1:
Input: 4->2->1->3 Output: 1->2->3->4Example 2:
Input: -1->5->3->4->0 Output: -1->0->3->4->5
- 풀이1_삽입 정렬
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def insertionSortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
cur = parent = ListNode(None)
while head:
while cur.next and cur.next.val < head.val:
cur = cur.next
cur.next, head.next, head = head, cur.next, head.next
cur = parent
return cur.next
Result
Runtime : 1956ms, Memory : 16.3MB
- 풀이2_삽입 정렬의 비교 조건 개선
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def insertionSortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# 초깃값 변경
cur = parent = ListNode(0)
while head:
while cur.next and cur.next.val < head.val:
cur = cur.next
cur.next, head.next, head = head, cur.next, head.next
# 필요한 경우에만 cur 포인터가 되돌아가도록 처리
if head and cur.val > head.val:
cur = parent
return parent.next
Result
Runtime : 164ms, Memory : 16.2MB
문제04 가장 큰 수
https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-number
항목들을 조합하여 만들 수 있는 가장 큰 수를 출력하라.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [10,2] Output: "210"Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,30,34,5,9] Output: "9534330"Example 3:
Input: nums = [1] Output: "1"Example 4:
Input: nums = [10] Output: "10"
- 풀이1_삽입 정렬
class Solution:
# 문제에 적합한 비교 함수
@ staticmethod
def to_swap(n1: int, n2: int) -> bool:
return str(n1) + str(n2) < str(n2) + str(n1) # 330 < 303 -> False // 3034 < 3430 -> True // 334 < 343 -> True // 305 < 530 -> True // 35 < 53 -> True // 345 < 534 -> True // 309 < 930 -> True // 39 < 93 -> True // 349 < 934 -> True // 59 < 95 -> True
# 삽입 정렬 구현
def largestNumber(self, nums: List[int]) -> str:
i = 1
while i < len(nums):# i = 1 -> 2 ->3->4->5, len(nums) = 5
j = i # j = 1 -> 2 ->3->4
while j > 0 and self.to_swap(nums[j - 1], nums[j]): # nums[1-1 = 0], nums[1] >> nums[2-1 = 1], nums[2] -> nums[1-1 = 0], nums[1] >> nums[3-1 = 2], nums[3] -> nums[2-1 = 1], nums[2] -> nums[1-1 = 0], nums[1] >> nums[4-1 = 3], nums[4] -> nums[3-1 = 2], nums[3] -> nums[2-1 = 1], nums[2] -> nums[1-1 = 0], nums[1]
nums[j], nums[j - 1] = nums[j - 1], nums[j] # pass -> [3,34,30,5,9] -> [34,3,30,5,9] -> [34,3,5,30,9] -> [34,5,3,30,9] -> [5,34,3,30,9] -> [5,34,3,9,30] -> [5,34,9,3,30] -> [5,9,34,3,30]-> [9,5,34,3,30]
j -= 1
i += 1
return str(int(''.join(map(str, nums)))) # [9,5,34,3,30] -> "9534330"
Result
Runtime : 76ms, Memory : 14.1MB
문제05 리스트 정렬
https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-anagram
t가 s의 애너그램인지 판별하라.
Example 1:
Input: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram" Output: trueExample 2:
Input: s = "rat", t = "car" Output: false
- 풀이1_정렬을 이용한 비교
class Solution:
def isAnagram(self, s: str, t: str) -> bool:
return sorted(s) == sorted(t)
Result
Runtime : 40ms, Memory : 15MB
문제06 색 정렬
https://leetcode.com/problems/sort-colors
빨간색을 0, 흰색을 1, 파란색을 2라 할 때 순서대로 인접하는 제자리 정렬을 수행하라.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,0,2,1,1,0] Output: [0,0,1,1,2,2]Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,0,1] Output: [0,1,2]Example 3:
Input: nums = [0] Output: [0]Example 4:
Input: nums = [1] Output: [1]
- 풀이1_네덜란드 국기 문제를 응용한 풀이
class Solution:
def sortColors(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
red, white, blue = 0, 0, len(nums)# red = 0, white = 0, blue = 6
while white < blue:
if nums[white] < 1:
nums[red], nums[white] = nums[white], nums[red] # 2) [0,0,2,1,1,2] 3) [0,0,2,1,1,2]
white += 1 # white = 1 -> 2
red += 1 # red = 1 -> 2
elif nums[white] > 1:
blue -= 1 # blue = 5 -> 4
nums[white], nums[blue] = nums[blue], nums[white] # 1) [0,0,2,1,1,2] 4) [0,0,1,1,2,2]
else:
white+=1 # white -> 3 -> 4
# 5) [0,0,1,1,2,2] 6) [0,0,1,1,2,2]
Result
Runtime : 32ms, Memory : 14.2MB
문제07 원점에서 K번째로 가까운 점
https://leetcode.com/problems/k-closest-points-to-origin
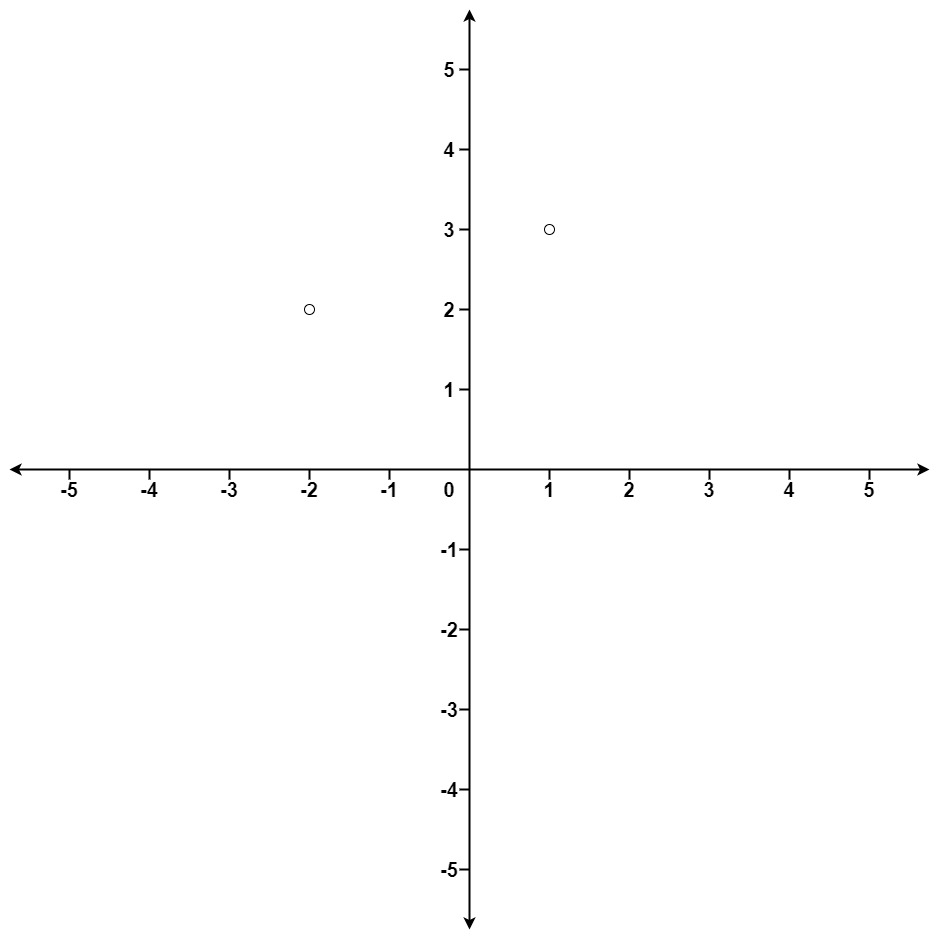
평면상에 points 목록이 있을 때, 원점(0, 0)에서 K번 가까운 점 목록을 순서대로 출력하라. 평면상 두 점의 거리는 유클리드 거리로 한다.
Example 1:
Input: points = [[1,3],[-2,2]], k = 1 Output: [[-2,2]] Explanation: The distance between (1, 3) and the origin is sqrt(10). The distance between (-2, 2) and the origin is sqrt(8). Since sqrt(8) < sqrt(10), (-2, 2) is closer to the origin. We only want the closest k = 1 points from the origin, so the answer is just [[-2,2]].Example 2:
Input: points = [[3,3],[5,-1],[-2,4]], k = 2 Output: [[3,3],[-2,4]] Explanation: The answer [[-2,4],[3,3]] would also be accepted.
- 풀이1_유클리드 거리의 우선순위 큐 순서
class Solution:
def kClosest(self, points: List[List[int]], k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
heap = []
for (x, y) in points:
dist = x ** 2 + y ** 2
heapq.heappush(heap, (dist, x, y))
# 가장 먼 거리를 구할 경우, heapq.heappush(heap, (-dist, x, y))
# heap = [(8, -2, 2), (10, 1, 3)]
result = []
for _ in range(k):
(dist, x, y) = heapq.heappop(heap)
result.append((x, y))
return result
Result
Runtime : 684ms, Memory : 20.3MB